6 Common Mistakes When Recording the Classical Guitar at Home, Part II
Part II - Post Processing
Professional sounding classical guitar at home is not a fantasy anymore or at least achieving a recording quality that is not embarrassing to share. Affordable audio interfaces, preamps and microphones have flooded the market these last decades, with increasing performance and processing power. Rooms, recording techniques and mixing are holding us back.
In the first part on the 6 Common Mistakes When Recording the Classical Guitar at Home, I tried to encourage you to try out different microphone positions and to study your room acoustics.
The second part focuses on some of the common mistakes of beginner classical guitar recordists on utilizing a proper signal chain and achieving satisfactory results in post-processing.
Mistake no.1 - Improper gain staging
AEA TRP2 Gain Knobs
The fear of clipping the converters leads some amateur recordists to use too little gain, resulting in recordings that are low in level. Without adequate signal-to-noise rations, these recordings will become noisy when any attempt is made to bring them at a normal level during mixing or playback. Contrarily, recording too “hot” will possibly clip the converters and can introduce nasty sonic artifacts to the audio. In either case, the recording will suffer from a limited dynamic range and high noise; attributes that we don't usually associate high-quality classical guitar recordings.
My advice is to aim between -6dB to -12dB as a maximum peak level (not average), per channel. Therefore, when you are happy with the placing and distance of your microphones, do a couple of test recordings, play as loud as you would normally do and set the gain levels accordingly. If you set the levels correctly, you will have a healthy and strong signal, but even if you (or another guitarist you are recording) eventually get carried away during the performance, you still have enough headroom to avoid digital clipping.
Mistake no.2 - Unrealistic panning
Classical guitar is a small instrument, radiating sound from a definite point in space. One of the worst choices you can make if you record in stereo (which you should) is to use a too wide panning. Regardless of if the listener is an audiophile type, sitting on his couch perfectly balanced in front of a pair of top-tier speakers, or a regular person listening to music with earbuds. A hard-panned left and right guitar will sound unnaturally wide and cloudy.
Proper panning of Stereo AB channels
A realistic classical guitar recording is one that creates a phantom image of the instrument right in the middle of the speakers, but with some space around it. Such recordings can remove the playback medium and transport the listener in the room with the player.
In typical AB Stereo scenarios, I pan one channel at 3 o'clock and the other at 9 o'clock. I fine-tune the panning according to the polar pattern of the microphones, how apart they are set, and the distance from the guitar.
Mistake no.3 - Limiting dynamics
Classical guitar is not the most dynamic instrument, and if anything, we should strive to capture as much dynamic range as possible (it starts from the player, so we should also prioritise dynamics in performance). Compressors, on the other hand, are designed to do just the opposite; minimize the dynamic information of an audio track by limiting the loudest notes and boosting the softest signal.
The classic Universal Audio limiting amplifier
Compressors do make the initial playback sound more exciting and powerful… for a few seconds, but in my opinion, it never pays back. Some of the problems that are introduced with the use of compressors in solo classical guitar recordings are squeezed dynamics, increased noise level and altered instrument tone.
Cross-genre guitarists employ compressors more often, as they learn that they can be invaluable in a dense mix. But I haven't found any use for dynamic limiting in a properly captured classical guitar recording.
Therefore, unless you have to deal with issues of the room or improper microphone positioning, don't use compressors on classical guitar recordings.
Mistake no. 4 - Being afraid of using filters
High-pass filter’s switch on an Austrian Audio OC18
Many microphones feature high-pass filters, the most common are 40Hz, 80Hz and 120Hz; the same is true for some dedicated outboard preamps. But many beginner recordists are afraid to take advantage of them. The truth is that in the context of the classical guitar, not much musical information is presented at the low-end frequencies. Most of what is below around 80Hz is unwanted room rumble and weird resonances; therefore by attenuating them, we end up with a cleaner recording. Capturing what is essential and leaving out the rest.
As low frequencies can have a lot of energy, it is preferable to cut undesirable low-end before the signal hits the converters, if possible. This tactic allows us to set the gain and levels appropriately and leads to better signal-to-noise ratios. But even if your microphones or preamps don't have any filters, you can still apply a high-pass filter in your DAW to remove non-essential information.
I also like to use a low-pass filter to remove high-end information that is inaudible, so that my audio consists of only the frequencies I can hear. A gentle roll-off of the low (below 50Hz) and high frequencies (above 18000Hz) is a good starting point. An EQ plugin with these basic filters is the first plugin I load on every track. You can read more on the article Three Most Essential Plugins for the Classical Guitar.
Mistake no.5 - Not learning how to use an equalizer
Other than the low- and high-end unwanted information that we can simply remove with the appropriate filters, undesirable resonances can occur in the audible range as well. These can be caused by the imperfect rooms that we are recording in, our instruments or our technique. Obnoxious resonances can and will distract the listener.
Learning how to use an equalizer to detect and attenuate or eliminate such issues will make the listening experience much more pleasurable.
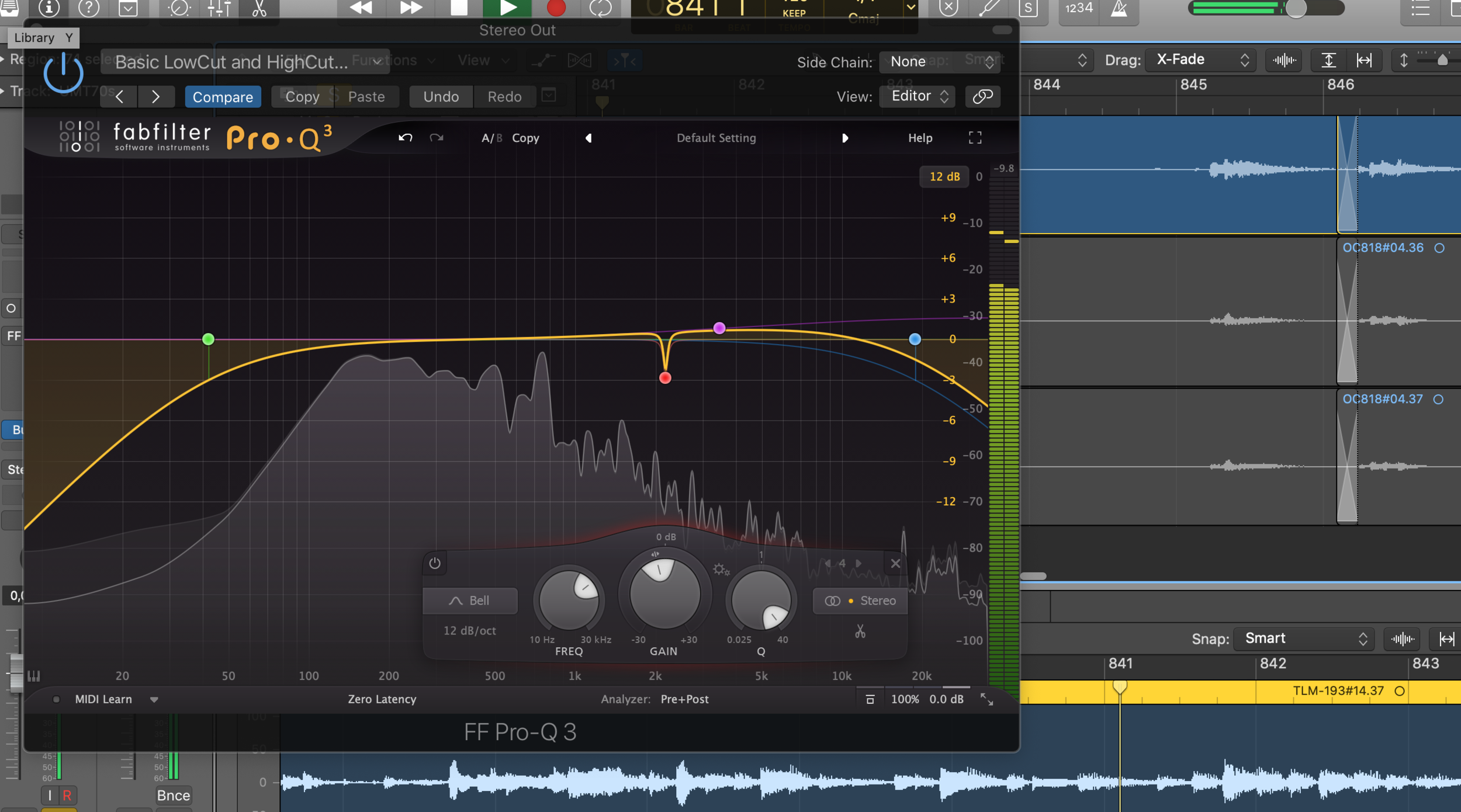
The best way to identify an offending frequency is by using your ears. I know that this doesn't sound like great advice, but keep reading. When you detect something that you don't like, add a bell-shaped point on your EQ with an extreme boost and search through the suspected range, like dialling in an analogue radio.
Once you find the irritating frequency, the sound should be quite disturbing at that point, apply a notch or a generous cut with a narrow Q. Toy around with the Q value to find the sweet spot; a setting that makes the problematic sound disappear but lets the rest of the audio unaffected.
FabFilter Pro-Q 3 with HP & LP Filters, a narrow Q Cut and a High Shelf Boost
Another use for an EQ is to change the overall balance of the recording. Sometimes you'd prefer a slightly fuller recording, or there is just a bit too much low-end. Perhaps the treble is a bit piercing, or you'd like to add some more clarity and articulation. Making gentle adjustments like these are generally uncomplicated with the use of Low or High Shelf adjustments. Just a couple of dB's can make a drastic difference to the evenness and impact of our music.
Just be careful not to overdo it, and always compare your mixes to your favourite recordings.
Finally, you can also use an equalizer to completely change the sound of an instrument and shape it to your liking. But if you've been diligent with the microphone positioning, and you like your guitar sound, you won't have to.
Mistake no.6 - Too much reverb
Placing the music into an artificial hall is a necessary lie
As I write on the Three Most Essential Plugins for the Classical Guitar article, nothing will affect the listener more than the physical space that the music takes place.
When we record at home, most rooms are not interesting enough, and so we need to enhance their sound with artificial reverb. But it is easy to overuse reverb, as it makes everything sound "better". Or so we think when we first enter the home recording world.
Most beginner recordists tend to choose a random church preset without any consideration to requirements of the music, tempo and other aesthetic choices. The result is a flood of unnatural and unattractive recordings which instead of sounding realistic or enchanted, they feel cheap.
Learn how the Time, Size and EQ settings found on your reverb plugin of choice to fine-tune the sound the ambience. Then turn down the Mix a little bit more than what you think it should be. Lastly, compare your efforts to commercial recordings (not that those are not guilty of overusing fake church algorithms).
Closing thoughts
Proper mixing can turn a decent recording into a great one
I hope that this article will make you more conscious of your post-processing choices. I need to write dedicated articles for the use of equalizers and reverb as there is a ton of things to discuss.
I know that many guitarists don't want to fuzz around with plugins, but proper audio processing can transform a recording. Mixing is an art in itself; a necessary evil that can turn a decent recording to a great one. Quality classical guitar recordings are important for your audience and benefit the classical guitar community as a whole. Thus, it's definitely worth the time and effort to learn how to mix your audio. Alternatively, you may search for someone else to do that for you.
Tip: You don't have to mix every track from scratch; after all, you probably record the same instrument with the same microphone technique and in the same room all the time. Create a template in your DAW with your basic panning, filter and reverb settings. You'll still have to tweak around a bit, as not every piece favours the same settings, nor every day is the same. Templates are great time savers.